Can CO2 Laser Cut Aluminum?
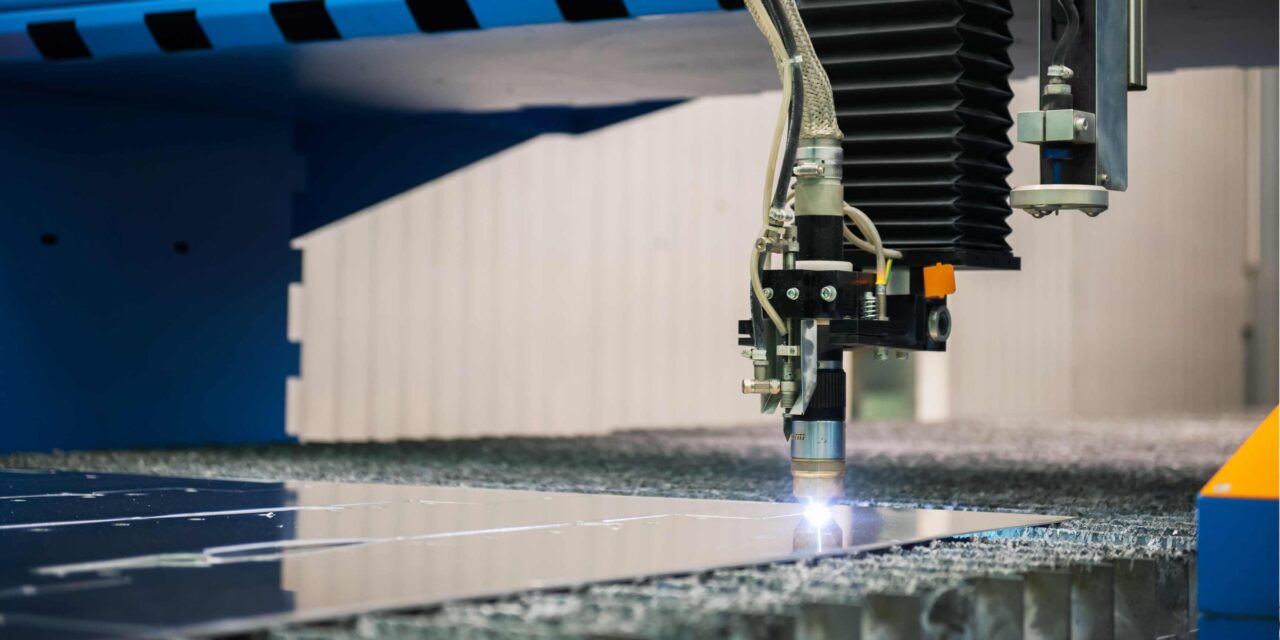

A brief on the characteristics and usage of CO2 laser and aluminum
Carbon dioxide lasers are cutting technology that is referred to as CO2 lasers in short form. Its nearly infrared lasers emit light using a CO2 gas mixture of nitrogen, hydrogen and CO2. This light is very intense and is employed in the process of heating or oxidizing a solid (material), for example, metal, wood or plastic.
Aluminum is a versatile metal used in structural drills; it has desirable physical/ mechanical and corrosion characteristics and is extensively utilized in aerospace, automobile and constructional applications. That is, the thermal and electrical conductivity of the metal can influence the laser-cutting process.
Characteristics of Aluminum and Its Adaptability to Laser Cutting
Because of the properties of aluminum, this material is somewhat difficult to apply with laser technology to cutting. It gives high reflectivity that a major part of the laser beam can be reflected off the surface without being absorbed. By reducing efficiency and more usage of energy, the cutting tools will wear out sooner and take more time to cut.
Secondly, aluminum creates a cover layer of oxidation on its surface and thus can act as a shield against rusting but also presents a challenge to the laser cutting process. This oxide layer needs to be passed through to allow the laser to cut through the metal and get an effective result.
How CO2 Lasers Work
CO2 lasers operate by passing current through gases inside a laser chamber. The excited gas releases its energy in the form of a laser beam, and this can be aimed and converged to bring about the required cutting topology. The energy from the beam is transferred to the stuff, in this case, heating the material and vibrating it enough to melt, evaporate or burn to make the cut desired.
Laser Cutting Aluminum: Advantages and Disadvantages
Using laser cutting in aluminum offers a number of advantages over conventional cutting techniques due to enhanced accuracy, a slim margin of heat-influenced area, and enhanced rates of cutting. These advantages may lead to the generation of improved quality parts and decreased manufacturing expenses. One limitation of laser cutting is that if aluminum, then it has limitations in reflective material as well as the coating chances with oxide layers.
Technical Issues Involving the Utilization of CO2 Laser for Cutting Aluminum
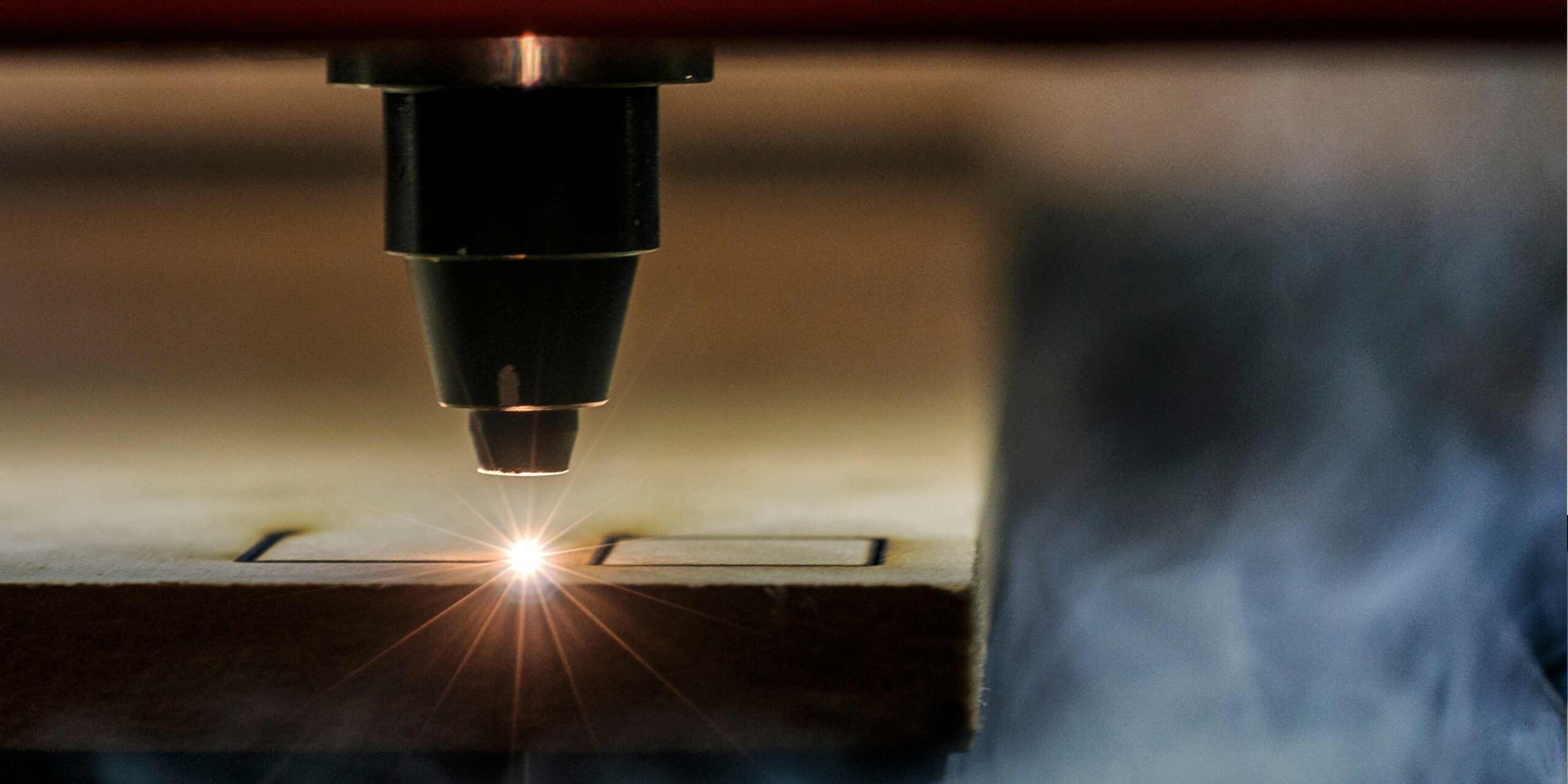
For a CO2 laser working the right technological parameters have to be there to enable proper cutting of the material.
These factors include:
– Laser power: It is possible to increase the density of the laser in order to avoid the influence of the aluminum’s high reflectivity and the presence of a thin oxide layer on its surface. This helps put the laser through the material in question, hence providing a cleaner cut through the item.
– Cutting speed: Using a low cutting speed will enable the laser beam to take sufficient time to permeate the material besides breaking through the oxide layer. It could cause a cleaner and a smoother incision.
– Assisting gases: Thus, to optimize the cutting process, an assisting gas can be applied to facilitate the removal of molten metal from the cutting area. The typical helping gases of laser-cutting aluminum are oxygen, nitrogen and air.
– Focus: During cutting aluminum it is very important to set the laser beam correctly. When the beam is well-focused, then expect a neat and accurate cut.
A comparison of CO2 Lasers with other laser types
But there are other types of lasers used in cutting aluminum, such as fibre laser and UV laser. In that case, these lasers may have advantages over CO2 lasers with respect to speed of cutting and utilization. But CO2 lasers also still count as popular because costs are relatively lower than most and can cut through most material types.
The typical uses of CO2 laser cutting of aluminum
CO2 laser cutting of aluminum is used in a wide range of industries and applications, including:
– Aerospace: Laser cutting is applied in the fabrication of accurate components of aircraft and spaceships.
– Automotive: Cars employ aluminum in the body and other parts, and cutting normally involves the use of CO2 lasers.
– HVAC: Today most of duct work, vents and other HVAC products are fabricated from aluminum using the laser cutting technique.
– Medical: Medical devices and equipment made of aluminum components are cut with the use of CO2 lasers.
– Architectural: Other applications of laser cutting include making clips and panels, metal cladding, and certain architectural embellishments.
